Understanding Psoriasis
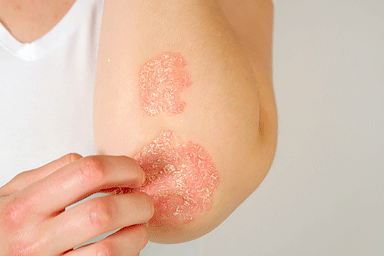
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes rapid skin cell buildup, leading to scaling, inflammation, and discomfort. These patches typically appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, or lower back, and can vary from mild to severe. While the exact cause remains unclear, genetics and immune system dysfunction play key roles. Environmental triggers such as stress, infections, cold weather, or certain medications can also cause flare-ups.
Treatment Options
Topical Treatments
For mild to moderate psoriasis, topical treatments are often the first line of defense. These include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, salicylic acid, and coal tar. They work by reducing inflammation, slowing skin cell growth, and removing scales.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. Narrowband UVB therapy is particularly effective, slowing the growth of affected skin cells. This treatment is suitable for moderate to severe cases and is often used when topical treatments are insufficient.
Systemic Medications
For severe psoriasis or cases unresponsive to other treatments, systemic medications may be prescribed. These include oral or injected drugs like methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics. Biologics target specific parts of the immune system and have shown significant efficacy in managing symptoms.
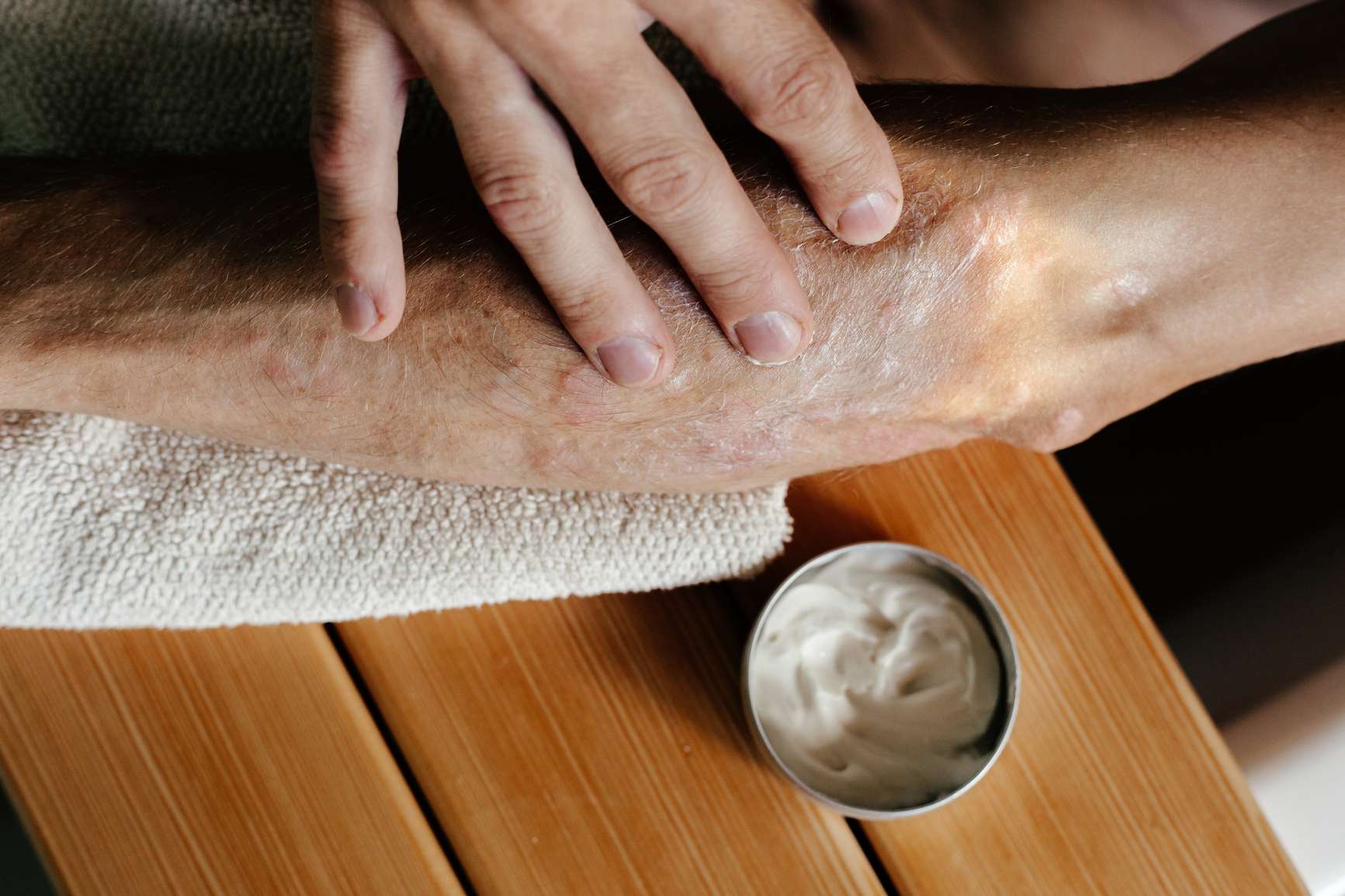
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can help manage psoriasis:
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated reduces dryness and scaling.
- Avoid Triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers like stress, smoking, and certain foods can prevent flare-ups.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods may alleviate symptoms.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can reduce stress-induced flare-ups.
Emerging Treatments
Recent advancements have introduced new treatments offering hope for those with psoriasis:
- Tapinarof: A topical cream approved for plaque psoriasis, it modulates the immune response and reduces inflammation.
- Deucravacitinib: An oral medication targeting specific immune pathways, showing promise in clinical trials.
These treatments provide additional options, especially for patients who have not responded to traditional therapies.
When to See a Doctor
If your symptoms are worsening, spreading, or not responding to over-the-counter treatments, it's important to consult a dermatologist. Early intervention can prevent complications like psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain and stiffness. A doctor can also help tailor a treatment plan that suits your specific condition, lifestyle, and medical history.
Living with Psoriasis
Managing psoriasis is about more than medication. It’s a long-term journey that often requires lifestyle changes and emotional support. Joining a psoriasis support group or online community can help you connect with others facing similar challenges. With proper care, many people are able to significantly reduce symptoms and enjoy a better quality of life.
Conclusion
Managing psoriasis requires a comprehensive approach combining medical treatments with lifestyle modifications. By working closely with healthcare providers and staying informed about emerging therapies, individuals with psoriasis can achieve better control over their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
Sources: