Early symptoms may often be mistaken for less serious illnesses, making awareness crucial. Detecting early signs can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Understanding Acute Leukemia
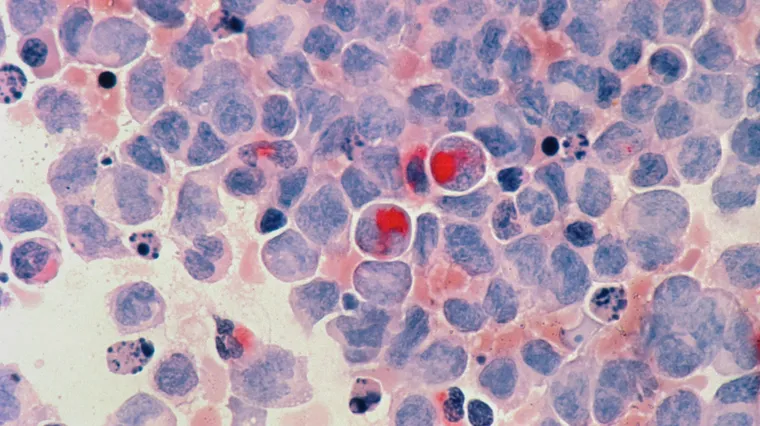
Acute leukemia is a swift and aggressive cancer of the blood and bone marrow. Unlike chronic leukemia that progresses slowly over time, acute leukemia develops rapidly, demanding immediate medical intervention. This condition originates in the bone marrow — the soft inner part of bones where blood cells are produced. Specifically, it results from an overproduction of immature white blood cells, which can obstruct the healthy production of red blood cells, platelets, and mature white blood cells. Consequently, the body’s ability to fight infections, control bleeding, and transport oxygen is significantly compromised.
There are two main types of acute leukemia: Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL). AML affects the myeloid cells that normally develop into different types of mature blood cells like red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. On the other hand, ALL impacts lymphoid cells that develop into lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell integral for immune responses. Though more prevalent in older adults, AML can also affect children, while ALL is the most common type of leukemia in children. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial in managing these life-threatening conditions, making it paramount to recognize the signs and symptoms early on.

Common Symptoms of Acute Leukemia
Acute leukemia can onset rapidly, with symptoms often developing within weeks. It's crucial to recognize the signs early to ensure prompt medical intervention. Common symptoms include extreme fatigue that doesn't improve with rest, unexplained weight loss, and frequent infections due to the body's lowered immune response. You might notice that your skin appears paler or washed out, and you could experience shortness of breath even after minimal exertion. Night sweats and a persistent high temperature, feeling hot or shivery, are also typical. These symptoms can be alarming, but being aware of them is the first step towards seeking necessary care.
In addition to the more apparent symptoms, you may experience unusual and frequent bleeding such as nosebleeds or bleeding gums. Bruising easily, without any obvious cause, and the appearance of flat red or purple spots on the skin are also indicators. Bone and joint pain, swollen glands in areas like your neck, armpit, or groin, and a persistent feeling of fullness or discomfort in the stomach are other signs to watch for. Because these symptoms overlap with various other conditions, seeking a professional medical opinion is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes.
Neurological Symptoms
Neurological symptoms in acute leukemia can be deeply concerning and often indicate that the disease has advanced or spread to other areas of the body. These symptoms can manifest as persistent headaches, sudden seizures, or noticeable changes in vision or balance. Some patients might also experience confusion or hallucinations, which can significantly impact daily life. These issues arise because the leukemia cells have started to infiltrate the brain or spinal cord, compromising their normal function.
In more severe cases, fluid buildup around the brain or in the chest can lead to shortness of breath or further compromise mental clarity. If you're noticing a combination of these symptoms, particularly alongside other common signs of acute leukemia, it’s vital to seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can be crucial in managing the neurological complications associated with acute leukemia, potentially improving both quality and length of life.