While tinnitus isn’t a disease itself, it is often a symptom of underlying conditions like hearing loss, stress, or ear injuries.Managing tinnitus requires a combination of medical interventions, lifestyle changes, and therapies. Treatments range from sound therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy to medications and alternative remedies. Although a complete cure is rare, many strategies help reduce the impact of tinnitus, improving overall quality of life.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is the perception of sound when no external noise is present. It can manifest as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or clicking sounds and may affect one or both ears. The condition varies in intensity and duration, with some individuals experiencing occasional episodes while others have persistent tinnitus.
Although tinnitus is commonly associated with age-related hearing loss, it can also result from exposure to loud noises, ear infections, medication side effects, or circulatory problems. Identifying the cause is crucial in determining the best treatment approach.
Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus has multiple causes, and understanding them can help in finding the right treatment:
- Hearing Loss – Age-related hearing decline or noise-induced damage can lead to tinnitus.
- Loud Noise Exposure – Frequent exposure to loud environments, such as concerts or construction sites, may trigger tinnitus.
- Ear Infections or Blockages – Earwax buildup, infections, or fluid accumulation can cause temporary or chronic tinnitus.
- Medications – Some drugs, like aspirin, antibiotics, or chemotherapy medications, may contribute to tinnitus as a side effect.
- Head or Neck Injuries – Trauma affecting the ear or brain can result in tinnitus.
- Circulatory Issues – High blood pressure or poor circulation may affect ear function, leading to tinnitus symptoms.
- Stress and Anxiety – Emotional stress can worsen tinnitus by increasing awareness of internal sounds.
Tinnitus Treatment Options
Although there is no universal cure for tinnitus, various treatments help manage symptoms and reduce its impact on daily life.
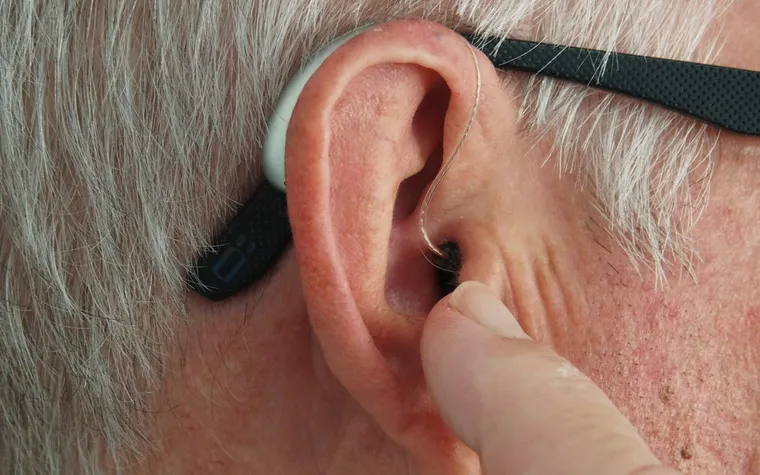
1. Hearing Aids
For individuals with hearing loss, hearing aids amplify external sounds, helping to mask tinnitus and improve overall hearing quality. Many modern hearing aids come with built-in sound therapy features.
2. Sound Therapy
Using external noise to mask tinnitus sounds is an effective treatment. White noise machines, nature sounds, or low-level background music can help distract the brain from tinnitus, making it less noticeable.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a psychological approach that helps individuals reframe negative thoughts about tinnitus. It reduces stress, improves coping mechanisms, and decreases the emotional impact of tinnitus.
4. Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT)
TRT combines sound therapy with counseling to retrain the brain to ignore tinnitus sounds. Over time, the brain learns to filter out the noise, reducing its prominence.
5. Medications
While no specific medication cures tinnitus, some drugs help manage associated symptoms. Anti-anxiety medications, antidepressants, and certain sleep aids can reduce stress and improve sleep, making tinnitus more bearable.
6. Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve tinnitus symptoms:
- Avoid loud noises: Protect ears from further damage by using earplugs in noisy environments.
- Reduce caffeine and alcohol: These stimulants may worsen tinnitus symptoms.
- Practice stress management: Relaxation techniques such as meditation and yoga help reduce tinnitus severity.
7. Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief through alternative treatments, including:
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest acupuncture may help reduce tinnitus intensity.
- Herbal Supplements: Ginkgo biloba and magnesium supplements are sometimes used, though scientific evidence is mixed.
- Chiropractic Care: For tinnitus caused by neck or jaw issues, chiropractic adjustments may provide relief.
When to See a Doctor
If tinnitus is persistent, worsening, or accompanied by dizziness, hearing loss, or pain, seeking medical attention is essential. A doctor can conduct hearing tests, examine underlying causes, and recommend appropriate treatments.
Conclusion
Tinnitus can be frustrating, but with the right treatments and lifestyle adjustments, its impact can be minimized. From hearing aids and sound therapy to cognitive techniques and medical management, various solutions exist to improve comfort and quality of life. If you experience tinnitus, consult a healthcare professional to explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs.